Neuromuscular Transmission/Train of Four Pod Monitors Neuromuscular Block with Confidence
The Smart Cable Neuromuscular Transmission (NMT) Pod quantitatively monitors the tactile muscle response to detect the electric stimulation through electromyography (EMG), helping clinicians make more informed decisions when neuromuscular blocking agents (NMBA) are used. The Nihon Kohden NMT Pod allows clinicians to objectively monitor the patient’s depth of paralysis during surgery when a neuromuscular blockade agent (NMBA), either nondepolarizing or depolarizing, is administered to the patient. Neuromuscular blockade has traditionally been monitored through acceleromyography (AMG), which relies on the clinician to count visual twitches from a patient’s thumb. These data are usually handwritten, or sometimes not recorded at all.
Nihon Kohden’s Smart Cable NMT Pod uses electromyography (EMG) to accurately capture the level of paralysis by peripheral nerve stimulation. The value and visualization of the Train of Four ratio is presented on the main screen of the host monitor. The hand-held controller is equipped with four quick keys that provide one-touch access to the most frequent functions, such as TOF and PTC. With the Smart Cable technology, the NMT pod integrates seamlessly into Nihon Kohden monitors (Life Scope G9, G7, G5 Max, G5, BSM-6000, and BSM-3500Series Bedside Monitors) via the AY/BSM-1700 input units, and patient data is automatically sent to the EMR patient record. This allows clinicians to use the data and the visual indicators on the screen to make better-informed decisions when NMBAs are used.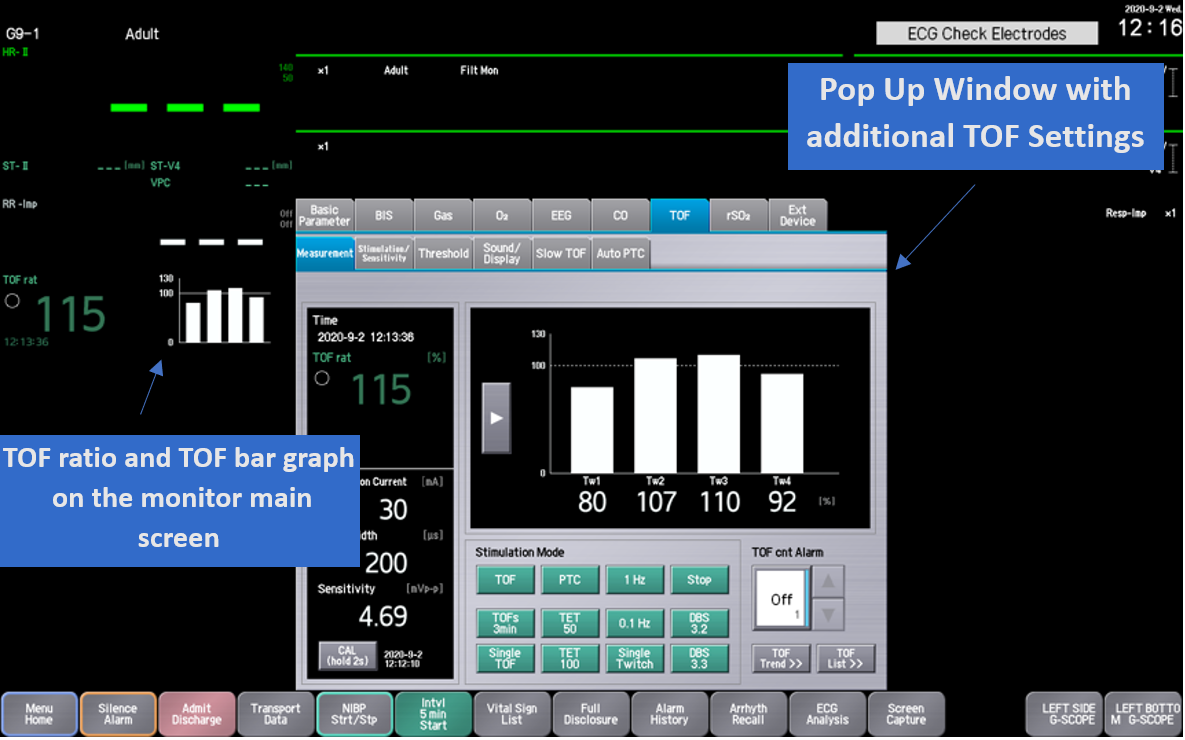
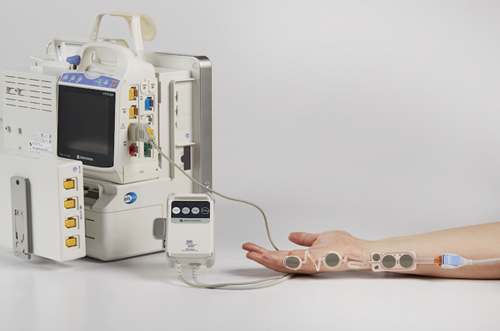
Click to see a larger image
The American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) recommends neuromuscular monitoring of neuromuscular blocking agents during and after general anesthesia. Inside the article,. The article states: “We recommend quantitative monitoring over qualitative assessment to avoid residual neuromuscular blockade.“



